Are you tired of skyrocketing energy bills and feeling overwhelmed by the technical jargon surrounding HVAC systems? You’re not alone.
Choosing the right heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to energy efficiency. Two popular contenders in this arena are Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems and traditional HVAC systems. But which one truly saves more energy?
We’ll simplify the complexities and dive into a head-to-head comparison between VRF and traditional HVAC systems. We’ll uncover the energy-saving secrets hidden within each option, helping you make an informed decision that could potentially save you a significant amount on your energy bills. Stick with us to discover which system aligns best with your needs and takes a lighter toll on your wallet. Let’s unlock the potential for a more efficient and cost-effective climate control solution for your space.
Introduction To Vrf And Traditional Hvac
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems are essential. They control indoor temperature and air quality. Two popular types are VRF and traditional HVAC. Each offers unique benefits and energy savings. Understanding these systems helps in making informed choices. Let’s dive into what makes them different.
What Is Vrf?
VRF stands for Variable Refrigerant Flow. It adjusts refrigerant flow to indoor units. This ensures precise temperature control. VRF systems are energy-efficient. They allow independent control of each zone. This means each room can have a different temperature. The system adapts to changes in the environment. This reduces unnecessary energy use.
Understanding Traditional Hvac Systems
Traditional HVAC systems are common in many buildings. They include a central unit. This unit distributes air through ducts. The system maintains a single temperature for all areas. Traditional systems are straightforward and reliable. But, they might use more energy. This happens because they condition all spaces equally. Even if not all areas are occupied.
Energy Efficiency Of Vrf Systems
VRF systems are highly efficient. They use variable-speed compressors. These compressors adjust to the building’s needs. This reduces energy waste. The ability to control zones individually boosts efficiency. This is especially true in larger buildings with varied usage patterns.
Energy Efficiency Of Traditional Hvac Systems
Traditional HVAC systems can be efficient, too. Newer models have improved energy ratings. Proper maintenance can enhance their efficiency. Yet, they might condition unoccupied spaces, wasting energy. System upgrades can help, but zone-specific control is limited.
Working Mechanism Of Vrf Systems
Understanding the working mechanism of Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems is key to appreciating their energy-saving potential. Unlike traditional HVAC systems, VRF uses a sophisticated approach to heating and cooling spaces. It adjusts the refrigerant flow according to the precise needs of each zone, optimizing energy usage and reducing waste.
How Vrf Systems Operate
VRF systems utilize advanced technology to regulate the flow of refrigerant to multiple indoor units. The outdoor unit changes the refrigerant flow based on the demands of each indoor unit. This means if one room needs more cooling while another needs less, the system adjusts accordingly.
Imagine your home on a hot summer day. You might want the living room to be cool and refreshing while preferring a warmer bedroom. VRF systems cater to these individual preferences without overworking the system. This flexibility is one of the reasons they are known for their energy efficiency.
Benefits Of Vrf’s Zoning Capability
VRF systems shine in their ability to create different zones within a building. Each zone can be independently controlled, allowing for personalized comfort. You won’t have to compromise between a chilly office and a warm meeting room.
This zoning capability not only enhances comfort but also saves energy. By not cooling or heating unnecessary spaces, VRF systems reduce power consumption significantly. Think of it as having a tailored experience, where every room feels just right.
Energy Efficiency: A Real-world Example
Consider a hotel with various guest preferences. Some guests may prefer cooler settings while others enjoy a warmer environment. VRF systems accommodate these diverse needs efficiently, reducing energy waste.
Hotels that have switched to VRF systems often report lower energy bills. The ability to precisely control temperatures in individual rooms means the system doesn’t overheat or overcool spaces unnecessarily. This adaptability is not just a technological marvel, but a practical solution to energy savings.
Maintenance And Longevity
Another advantage of VRF systems is their low maintenance requirements. With fewer moving parts and less stress on the system, they tend to have a longer lifespan compared to traditional HVAC systems.
Regular check-ups are essential, but the overall maintenance cost is often lower. This longevity paired with reduced energy bills can make VRF systems a financially attractive option. Wouldn’t you prefer investing in a system that promises long-term savings and reliability?
As you weigh the options between VRF and traditional HVAC systems, consider how much energy you could save. Could this be the smarter choice for your home or business?
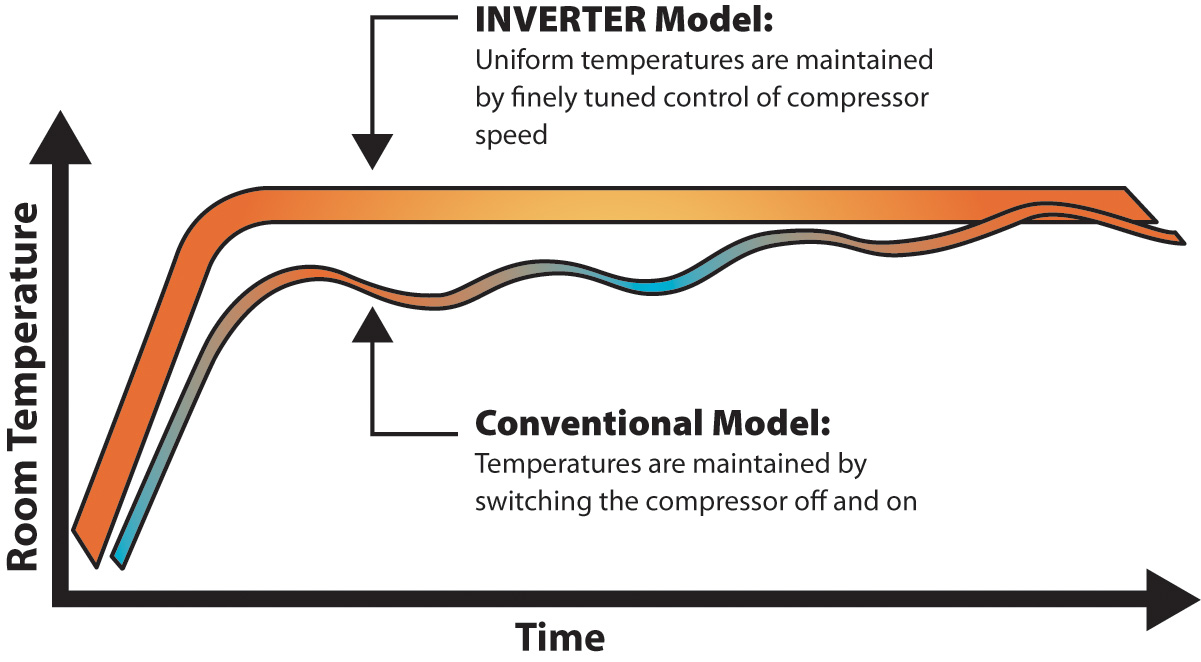
Functionality Of Traditional Hvac
Traditional HVAC systems operate by cycling on and off to maintain temperature. This consumes more energy compared to VRF systems, which adjust refrigerant flow for efficiency.
When considering the energy-saving potential of HVAC systems, understanding the functionality of traditional HVAC is crucial. You might have experienced the comforting hum of air conditioning units during a sweltering summer. These systems are familiar, often seen in homes and offices. But have you ever wondered how they work and what makes them tick? Let’s dive into the core functions of traditional HVAC systems.Heating And Cooling Mechanisms
Traditional HVAC systems typically consist of separate units for heating and cooling. The heating element often relies on a furnace or a heat pump, while cooling is managed by a central air conditioning unit. Each component is dedicated to its specific function, which can sometimes lead to inefficiencies. Imagine your home furnace working hard during winter, only for the air conditioning to pick up the slack in summer. This constant toggling between systems might not be the most energy-efficient way to maintain comfort.Air Distribution Process
Air distribution in traditional HVAC systems is primarily managed through a network of ducts. These ducts transport air from the central unit to various rooms in your home or office. Ductwork can be a double-edged sword. While it facilitates the flow of conditioned air, any leaks or blockages can lead to energy loss. Have you ever felt a room was colder or warmer than the rest of the house? That’s often due to uneven air distribution, which can result in higher energy consumption as the system tries to compensate.Temperature Control Options
Most traditional HVAC systems offer basic temperature control through a thermostat. You set the desired temperature, and the system works to achieve it. But here’s the catch: these systems usually maintain a single temperature setting across the entire space. This means you might find yourself pulling on a sweater in one room while another feels perfectly comfortable. It raises the question—are you wasting energy heating or cooling areas unnecessarily?Maintenance And Energy Efficiency
Regular maintenance is vital for traditional HVAC systems to function efficiently. Things like changing filters, cleaning ducts, and servicing units can prevent energy waste. Yet, many people neglect these tasks, leading to higher energy bills. Have you checked your HVAC system lately? Keeping it in top shape might save you money and energy. In understanding these functionalities, ask yourself: Is your traditional HVAC system serving your energy-saving goals?Energy Efficiency Factors
Choosing between VRF and traditional HVAC systems means understanding energy efficiency factors. Each system has its own strengths and weaknesses. These factors determine how much energy you save. Energy efficiency impacts costs and the environment. Learn how component efficiency, system design, and climate affect energy usage.
Component Efficiency
Component efficiency is crucial for energy savings. VRF systems use advanced compressors. These compressors adjust power based on demand. Traditional HVAC systems often run at full capacity. This leads to more energy use. Efficient components reduce waste. VRF systems often have better component efficiency.
System Design And Layout
System design influences energy efficiency. VRF systems offer flexible designs. They adapt to building layouts. This flexibility reduces energy waste. Traditional HVAC systems have fixed designs. They may not fit all spaces perfectly. Proper design saves energy. VRF systems excel in adaptable layouts.
Climate And Environmental Impact
Climate affects energy efficiency. VRF systems work well in varied climates. They adjust to temperature changes. Traditional HVAC systems struggle in extreme weather. Environmental factors also play a role. VRF systems often have eco-friendly features. These features reduce carbon footprints. Climate adaptability is key for energy savings.
Cost Implications
Comparing VRF and traditional HVAC systems highlights cost differences in energy savings. VRF systems often reduce energy bills due to their efficiency and flexibility. Traditional HVAC systems may incur higher costs with less adaptability to varying temperatures.
When deciding between a VRF (Variable Refrigerant Flow) system and a traditional HVAC system, understanding the cost implications is crucial. Both systems come with their unique financial demands, which can significantly affect your budget. Let’s break down these costs into three main areas: installation, maintenance, and long-term savings.Installation Costs
The initial cost is often the first hurdle homeowners face. VRF systems generally have higher upfront costs compared to traditional HVAC systems. This is due to their complex technology and the need for specialized installation. However, the higher cost can be justified by the efficiency and flexibility VRF systems offer. Traditional systems might be cheaper to install, but they can lack the precision and adaptability of a VRF system. It’s essential to weigh the initial cost against potential benefits. Would you prefer a system that’s cheaper now, or one that could save you more down the line?Maintenance Expenses
Maintenance is another area where costs can vary significantly between the two systems. VRF systems, being more advanced, typically require specialized technicians for service and repairs. This can potentially lead to higher maintenance costs. On the other hand, traditional HVAC systems are simpler and often easier to service. This can mean lower maintenance costs, but it could also imply more frequent repairs due to wear and tear. Which system aligns better with your maintenance budget? Consider both the frequency and cost of servicing.Long-term Savings
Long-term savings is a critical factor that might sway your decision. VRF systems are known for their energy efficiency, which can lead to substantial savings on energy bills over time. Their ability to adjust output based on demand means less energy waste. In contrast, traditional systems might not offer the same level of efficiency. They can consume more energy, especially if they are not properly maintained or are outdated. Could the savings in energy bills over the years justify the higher initial cost of a VRF system for you? Reflect on your long-term financial goals and energy consumption patterns. Choosing between a VRF and a traditional HVAC system involves more than just comparing price tags. It’s about understanding the full financial picture and how each option aligns with your specific needs and budget. Make sure to consider both immediate costs and future savings to make the best decision for your home.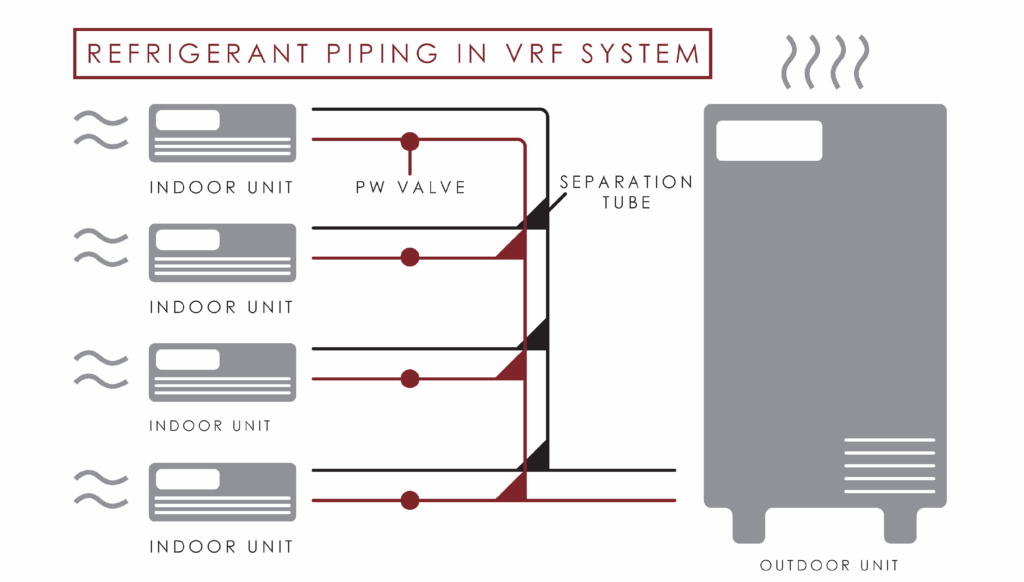
Credit: www.csemag.com
Performance In Different Climates
Choosing the right HVAC system depends on your climate. Different climates affect HVAC performance. VRF (Variable Refrigerant Flow) systems and traditional HVAC systems react differently. Energy efficiency varies across climates. Understanding these differences helps in making informed choices.
Cold Climates
Cold climates demand efficient heating systems. VRF systems excel in these conditions. They provide precise heating. This leads to reduced energy consumption. Traditional HVAC systems often struggle. They can be less efficient in cold weather. VRF systems adjust to temperature changes. This ensures consistent comfort. Energy savings become noticeable.
Warm Climates
Warm climates require effective cooling. Traditional HVAC systems often consume more energy. They work harder to maintain cool temperatures. VRF systems adapt well to heat. They offer variable cooling. This reduces energy usage. VRF technology optimizes performance. It adjusts to varying heat levels. This results in lower energy bills.
User Experience And Comfort
When deciding between VRF and traditional HVAC systems, user experience and comfort are key factors to consider. Both systems aim to maintain a pleasant environment, but they do so in different ways. Your choice may depend on your priorities for temperature control and noise levels.
Temperature Control
Imagine waking up in a room that’s just the right temperature—VRF systems make this possible with their precise control. They allow you to adjust temperatures in different areas of your home independently. This means you can keep your bedroom cooler while your living room stays warm.
Traditional HVAC systems often struggle with this level of precision. They usually maintain a consistent temperature throughout the house, which can lead to discomfort in certain areas. Have you ever felt too cold in one room while the rest of your house feels just right?
With VRF, you have the flexibility to tailor comfort to each room’s unique needs, offering a personalized experience. Isn’t it great to have control over your comfort without compromise?
Noise Levels
Have you ever been jolted awake by the loud hum of your HVAC system kicking in? Traditional systems can be noisy, disrupting your peace and quiet. They can be particularly bothersome at night when you’re trying to sleep.
VRF systems, on the other hand, are known for their quiet operation. They maintain a serene environment, ensuring you can focus on your work or relax without interruption. Many VRF users appreciate the tranquility it brings to their homes.
Think about how much more enjoyable your daily routine could be without the constant background noise. Isn’t silence the soundtrack to a more comfortable living space?
As you weigh your options, consider what matters most to you in terms of user experience and comfort. Do you value precise temperature control and a quiet atmosphere? These factors could significantly influence your decision between VRF and traditional HVAC systems. Your comfort is personal, and choosing the right system can greatly enhance your home environment.
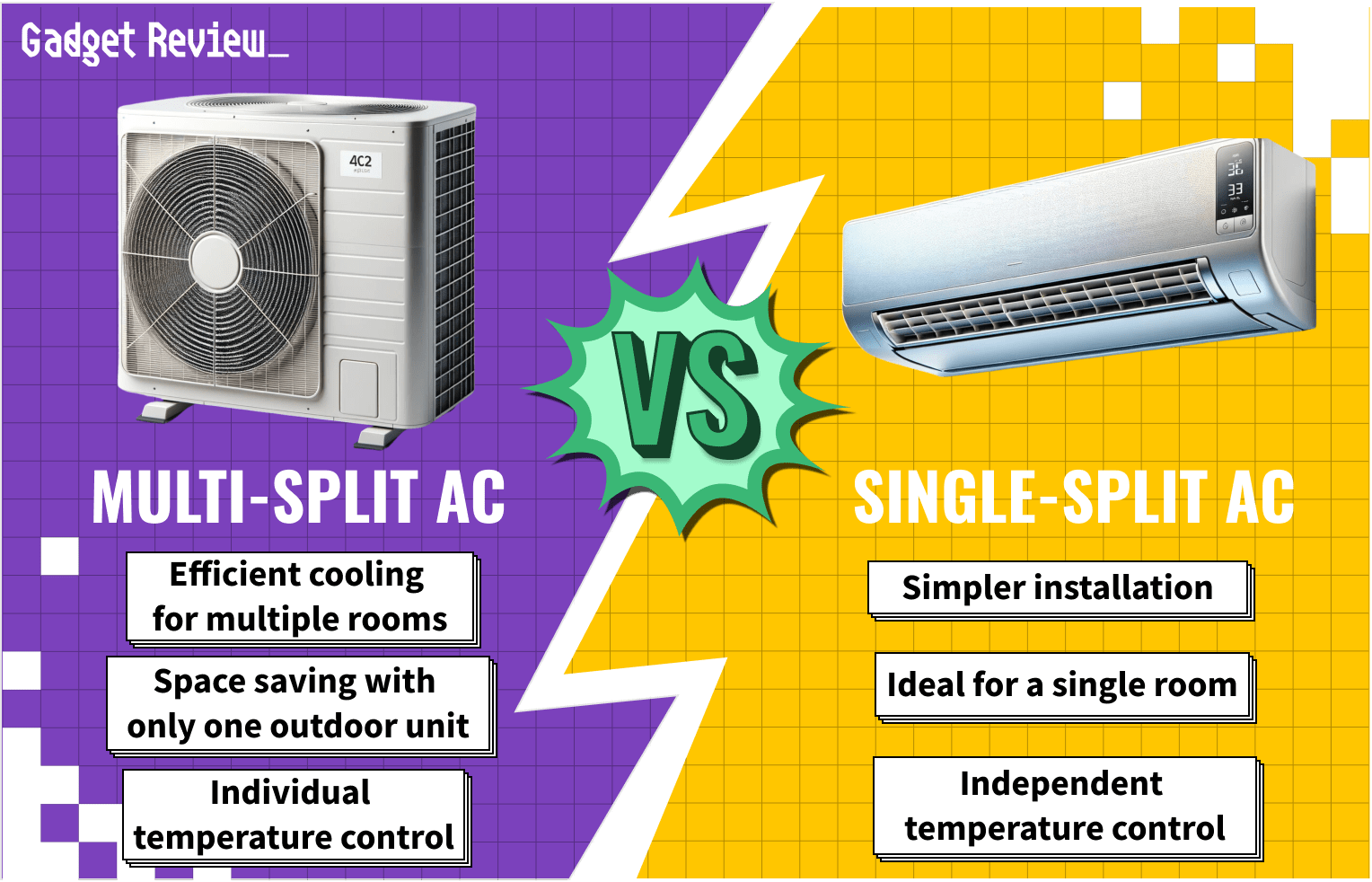
Credit: www.gadgetreview.com
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements shape how we manage energy consumption. VRF systems, known as Variable Refrigerant Flow, and traditional HVAC systems reflect this change. Understanding these advancements helps homeowners and businesses decide which saves more energy. Both systems have unique features impacting energy efficiency.
Vrf Systems: Precision Control
VRF systems offer precision control over heating and cooling. They adjust refrigerant flow based on specific room needs. This minimizes energy waste and enhances comfort. Each indoor unit operates independently. It provides tailored temperatures in different zones.
Traditional Hvac: Consistent Performance
Traditional HVAC systems deliver consistent performance. They use a single thermostat to control temperature. This setup provides uniform heating and cooling. It suits spaces with constant occupancy. Their simplicity appeals to those preferring straightforward operation.
Smart Sensors And Automation
Modern systems integrate smart sensors and automation. Sensors detect room occupancy and adjust settings automatically. This reduces unnecessary energy use. Automation enhances convenience and efficiency. Users experience optimal comfort without manual adjustments.
Energy Monitoring Tools
Energy monitoring tools track consumption in real-time. These tools identify patterns and inefficiencies. Users can make informed decisions to save energy. Both VRF and traditional systems can utilize these tools. They offer insights into energy-saving opportunities.
Case Studies And Real-world Examples
Understanding the energy efficiency of HVAC systems is crucial. With rising energy costs, choosing the right system matters. This section explores case studies and real-world examples comparing VRF and traditional HVAC systems. See how these systems perform in actual settings.
Case Study: Office Building In New York
An office building in New York upgraded from traditional HVAC to VRF. The change led to energy savings of 30%. Employees noticed improved air quality. Utility bills decreased significantly. This example highlights VRF’s energy-saving potential.
Real-world Example: Residential Complex In California
A residential complex in California opted for VRF systems. Energy bills dropped by 25%. Residents reported better temperature control. This choice also minimized maintenance needs. The shift proves VRF’s efficiency in residential settings.
Case Study: Hotel In Miami
A Miami hotel replaced its HVAC system with VRF technology. The hotel saved 35% on energy costs. Guests experienced enhanced comfort. The hotel management praised the system’s flexibility. This case illustrates VRF’s benefits for hospitality venues.
Real-world Example: School In Texas
A Texas school chose VRF over traditional HVAC. The decision reduced energy expenses by 40%. Classroom climates improved. Teachers noted increased student concentration. This example demonstrates VRF’s effectiveness in educational institutions.

Credit: www.lg.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Vrf Consume More Electricity?
VRF systems can be more energy-efficient compared to traditional HVAC systems. They adjust cooling and heating based on demand, potentially reducing electricity consumption. Energy savings depend on usage patterns, system maintenance, and installation quality. Always consult an HVAC professional for an accurate assessment of your specific needs.
What Is The Most Energy Saving Hvac System?
The most energy-saving HVAC system is a geothermal heat pump. It efficiently uses the earth’s natural temperature to heat and cool. Consider ductless mini-split systems for smaller spaces, offering flexibility and energy savings. Regular maintenance and smart thermostats enhance efficiency further.
Does Vrf Save Energy?
Yes, VRF systems save energy by adjusting refrigerant flow based on demand. They provide efficient heating and cooling. VRF technology reduces energy consumption and operating costs. It offers precise temperature control and is ideal for commercial and residential buildings. Energy savings can reach up to 30% compared to traditional systems.
Is Vrf Better Than Hvac?
VRF systems offer energy efficiency and flexible zoning, making them ideal for varied climate needs. HVAC systems provide consistent airflow and are cost-effective for simpler installations. Choose VRF for complex buildings requiring precision control; opt for HVAC for straightforward projects with budget constraints.
Consider your specific requirements for optimal choice.
Conclusion
Choosing between VRF and traditional HVAC depends on your energy goals. VRF systems can offer better efficiency, saving more energy. Traditional systems, though, might suit smaller spaces. Cost factors play a role too. Consider installation and maintenance expenses. VRF might have higher upfront costs.
Traditional systems are often easier to install. Think about long-term savings and environmental impact. Energy efficiency benefits the planet. Evaluate your needs and budget carefully. Both systems have pros and cons. Make an informed decision for your space. Choose what fits best for comfort and savings.